

The proglottids, for instance, are not regenerative rather they carry and release a large number of eggs and die. However, strobilation products represent indirect reproduction. It involves each portion regenerating missing parts to become a completely new organism. Planarian fission and fragmentation generally portray direct reproduction. In paramecium, fission is a transverse type and is said to be an oblique type in organisms like ceratium.įurthermore, few metazoan species undergo body division similar to binary fission called fragmentation. Whereas, fission can be a longitudinal type in organisms like the euglena. In certain organisms like the amoeba, fission is an irregular type because the cell separation is along any plane. The ephyrae and the proglottids all mature and eventually separate from the strobilus end. In tapeworms, the fission products are the proglottids while in scyphozoan jellyfish it is the ephyrae. Strobilation usually gives rise to a chain of fission products referred to as strobilus. The regular transverse fission is called strobilation in some organisms like tapeworms and scyphozoan jellyfish polyps. We have two types of binary fission in protists which include transverse fission and longitudinal fission. In this reproduction, an organism duplicates its genetic material, or deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), and as it divides into two as each new organism receives one copy of the DNA.įurthermore, depending on the axis of cell separation, there are about four types of binary fission. This asexual reproduction is the primary means of reproduction in prokaryotes. In binary fission, the process at which the parent cell divides into two daughter cells is known as cytokinesis. Bacteria to be able to remain viable and competitive tend to divide and provide each offspring with a complete copy of their genetic material. Typical examples of organisms that reproduce via binary fission include cyanobacteria, eubacteria, paramecium, amoeba, and archaea. Many prokaryotes and some eukaryotes reproduce via binary fission and some organelles in the cell such as mitochondria through the process of binary fission undergo cell division. This reproduction is asexual because it doesn’t involve the fusion of sex cells or gamete. A survey of mitotic assembly components found in present-day unicellular eukaryotes reveals crucial intermediary steps to the complex membrane-enclosed genomes of multicellular eukaryotes.This fission is different from other fission in that the process involves the formation of only two cells from, a parent cell. While both proteins are found in extant organisms, tubulin function has evolved and diversified tremendously since evolving from its FtsZ prokaryotic origin. In this example, FtsZ is the ancestor protein to tubulin (a modern protein). In addition, both FtsZ and tubulin employ the same energy source, GTP (guanosine triphosphate), to rapidly assemble and disassemble complex structures.įtsZ and tubulin are homologous structures derived from common evolutionary origins. FtsZ proteins can form filaments, rings, and other three-dimensional structures that resemble the way tubulin forms microtubules, centrioles, and various cytoskeletal components. However, the FtsZ protein that plays such a vital role in prokaryotic cytokinesis is structurally and functionally very similar to tubulin, the building block of the microtubules that make up the mitotic spindle fibers that are necessary for eukaryotes.
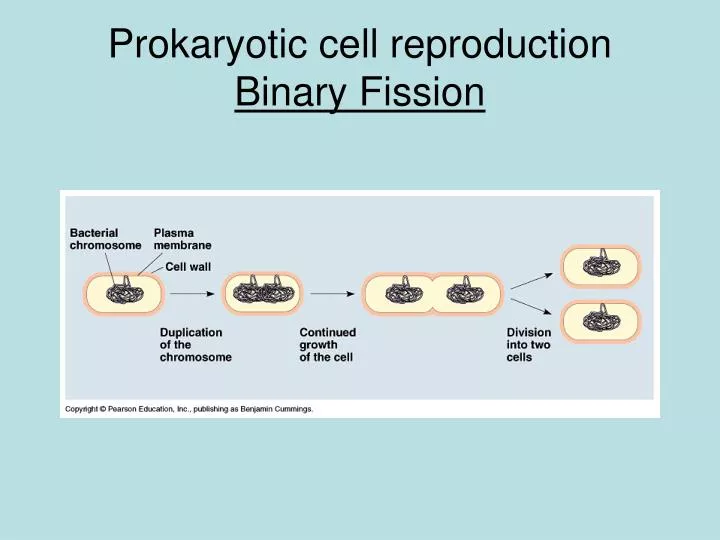
Prokaryotic cells, on the other hand, do not undergo karyokinesis and, therefore, have no need for a mitotic spindle. The precise timing and formation of the mitotic spindle is critical to the success of eukaryotic cell division. \( \newcommand\): Binary Fission: These images show the steps of binary fission in prokaryotes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
